The Issue of Water Scarcity for Industrial Producers
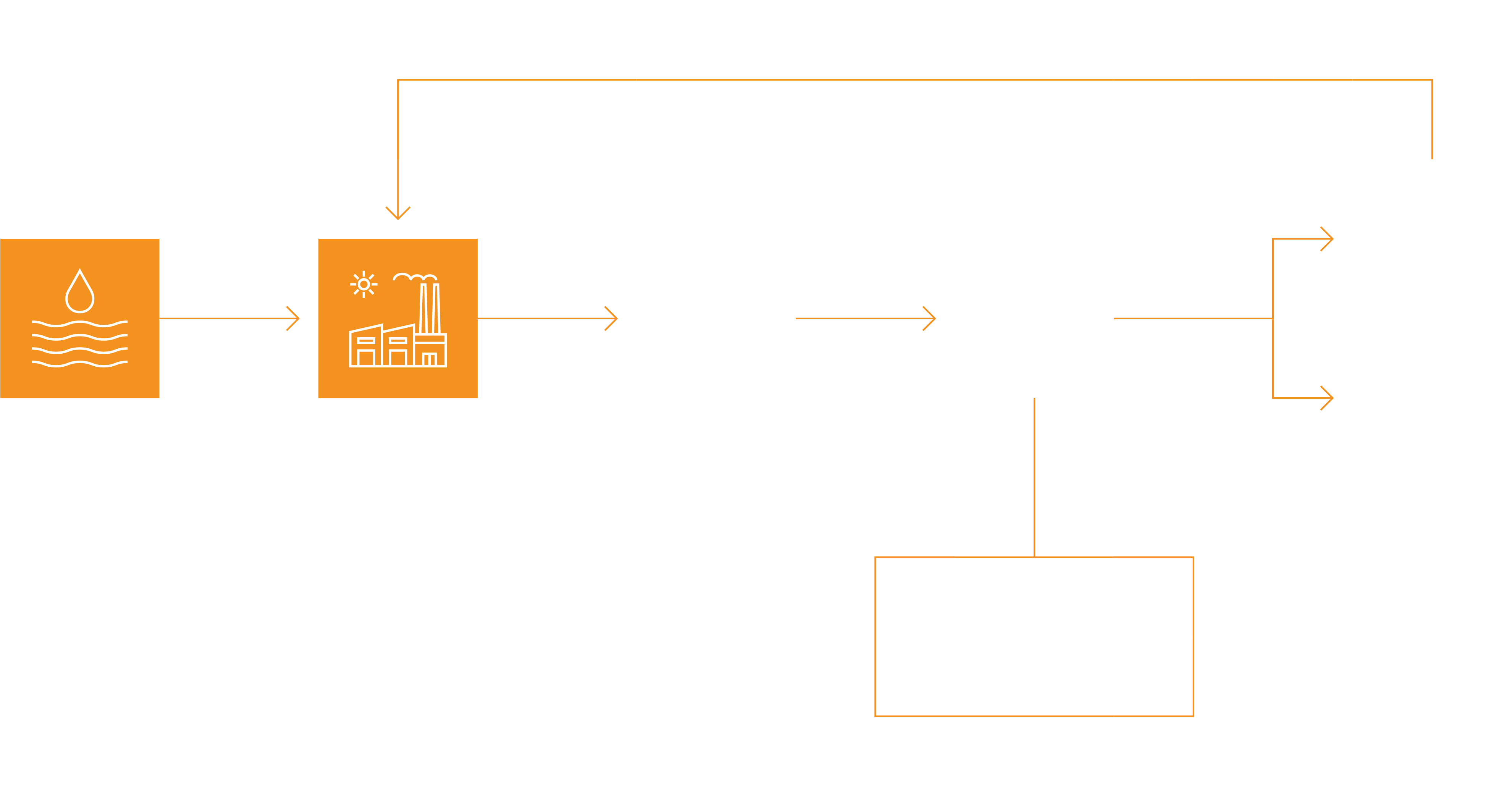
Fresh water is essential to industry, but for many producers it is scarce and costly to access. With climate change, tightening regulations, and other evolving challenges at play, the issue of water scarcity is becoming increasingly acute.
Drought, climate change, and industrial overuse can deplete local water resources.
Water is used for cleaning, lubrication, and cooling — there is no viable substitute for industry.
Competition for local water resources can cause tension between industrial producers and local communities.
Many industrial producers are under pressure from tightening regulations.
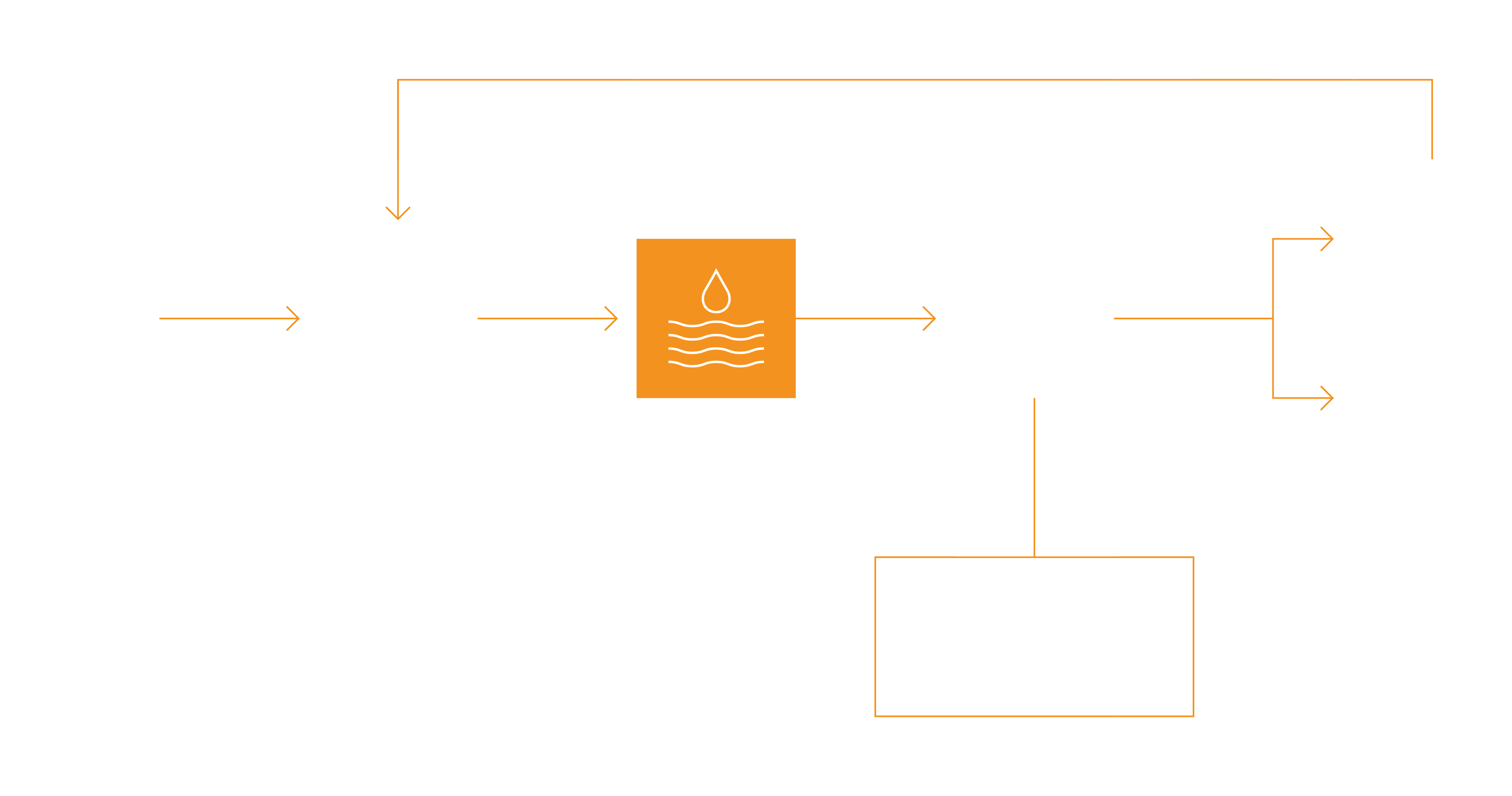
Zero Liquid Discharge Wastewater Treatment as a Solution
The Zero liquid discharge (ZLD) treatment process transforms wastewater into reusable clean water and solid waste. This process enables industrial producers to access clean water whilst reducing their net water consumption and costs.
Treatment energy costs can be high for ZLD, however onsite renewable energy can offer a decarbonised solution.
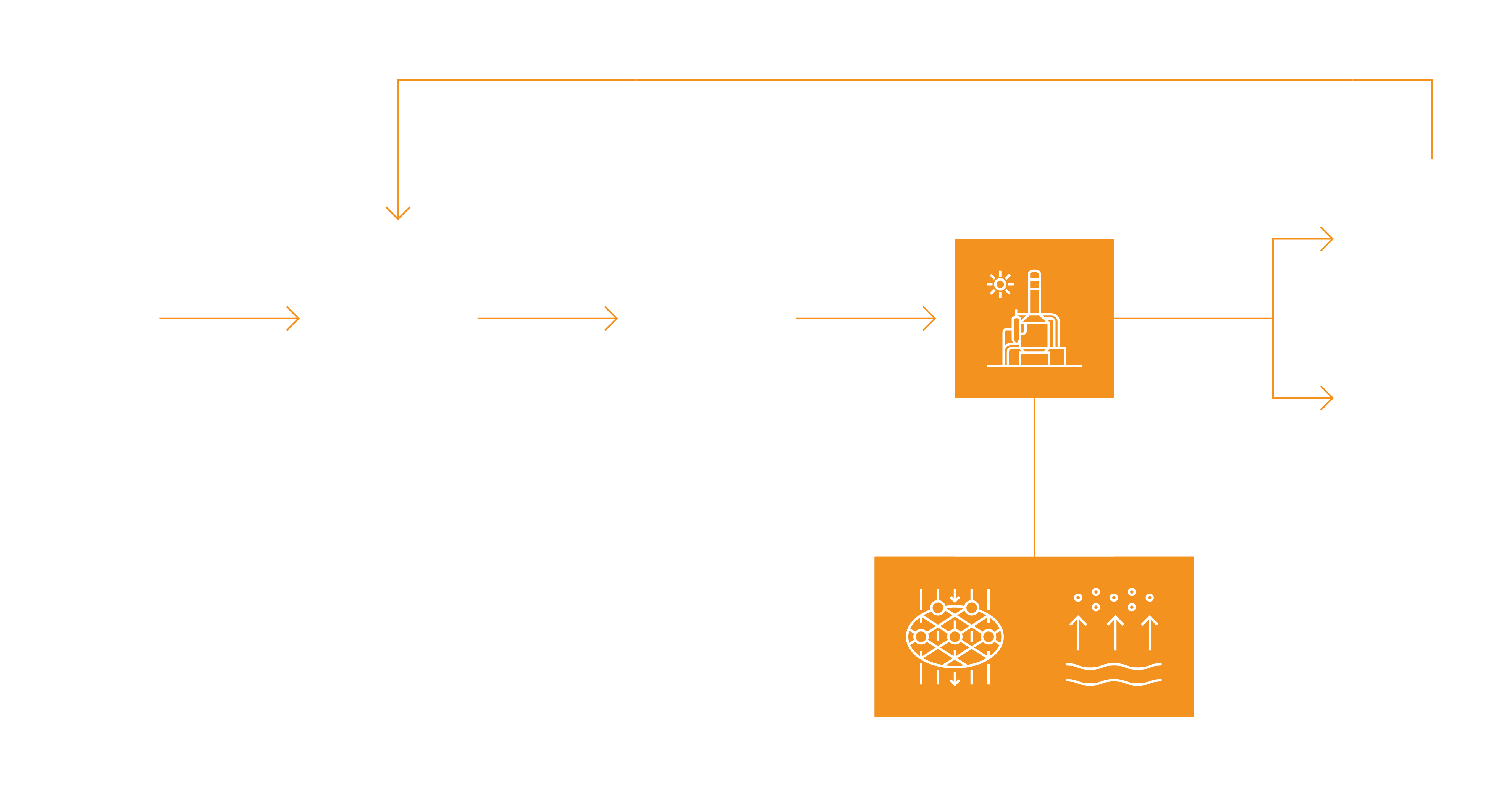
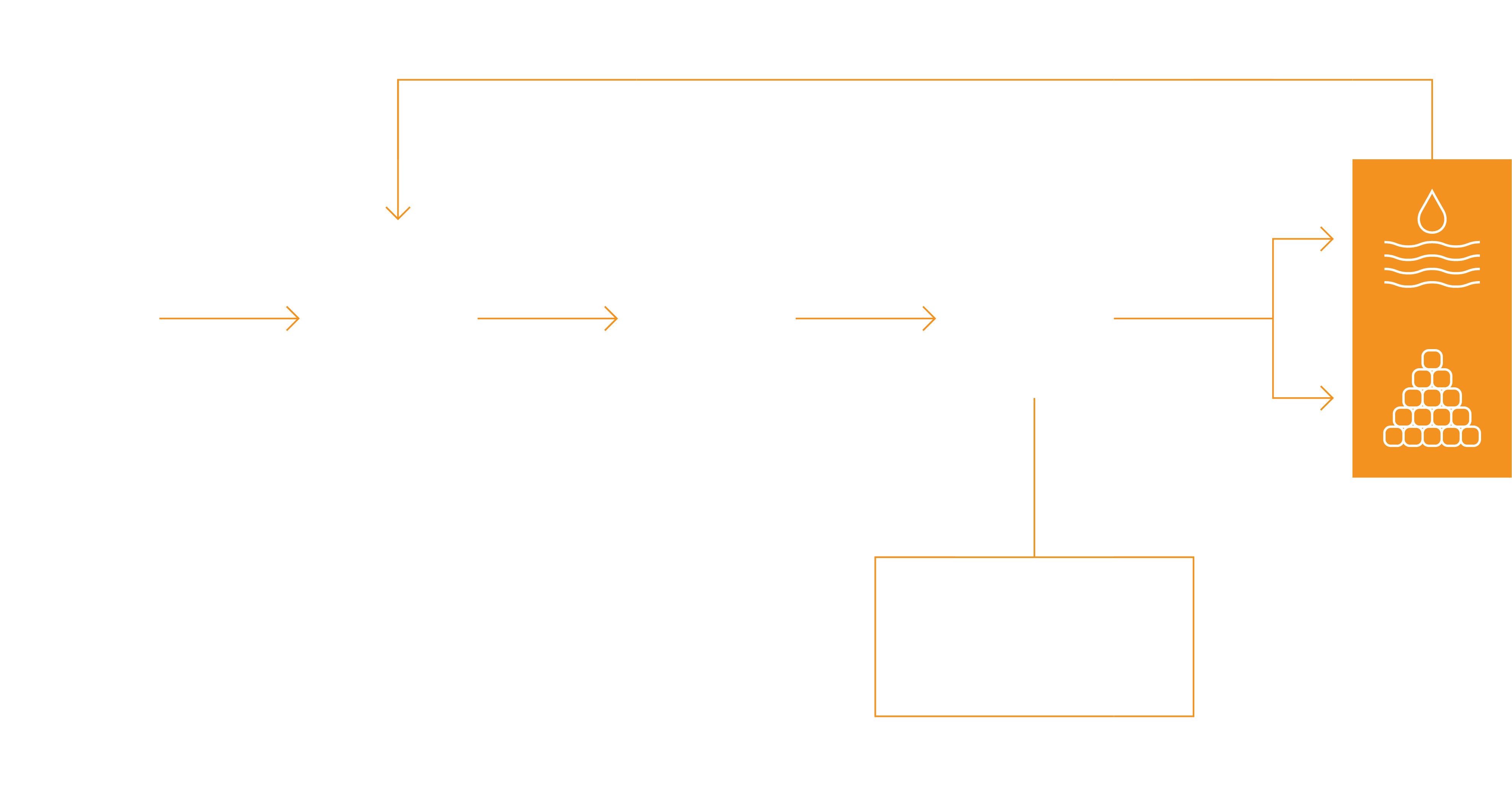
How Zero Liquid Discharge Wastewater Treatment Works
Project SY
Asset: Water Reuse Plant
Location: China
Production: 50,000m3/day
Tangshan, Hubei province, China, is a water-stressed area where there is insufficient fresh water to meet the needs of local industry and settlements. Local authorities have enforced withdrawal limits to reduce industry’s draw of local aquifers which are becoming salinated from over-extraction.
The Water Reuse Plant can reclaim 50,000m3/day of reuse water for the clients’ production, using biological filter, microfiltration, reverse osmosis and ion exchange processes.